Statistical or Non Statistical Sampling Which Approach Is Best
Define statistical and non-statistical sampling. The most common non-statistical sampling methods used in audits alpha sample time -based sample and systematic sampleare explained in IV.
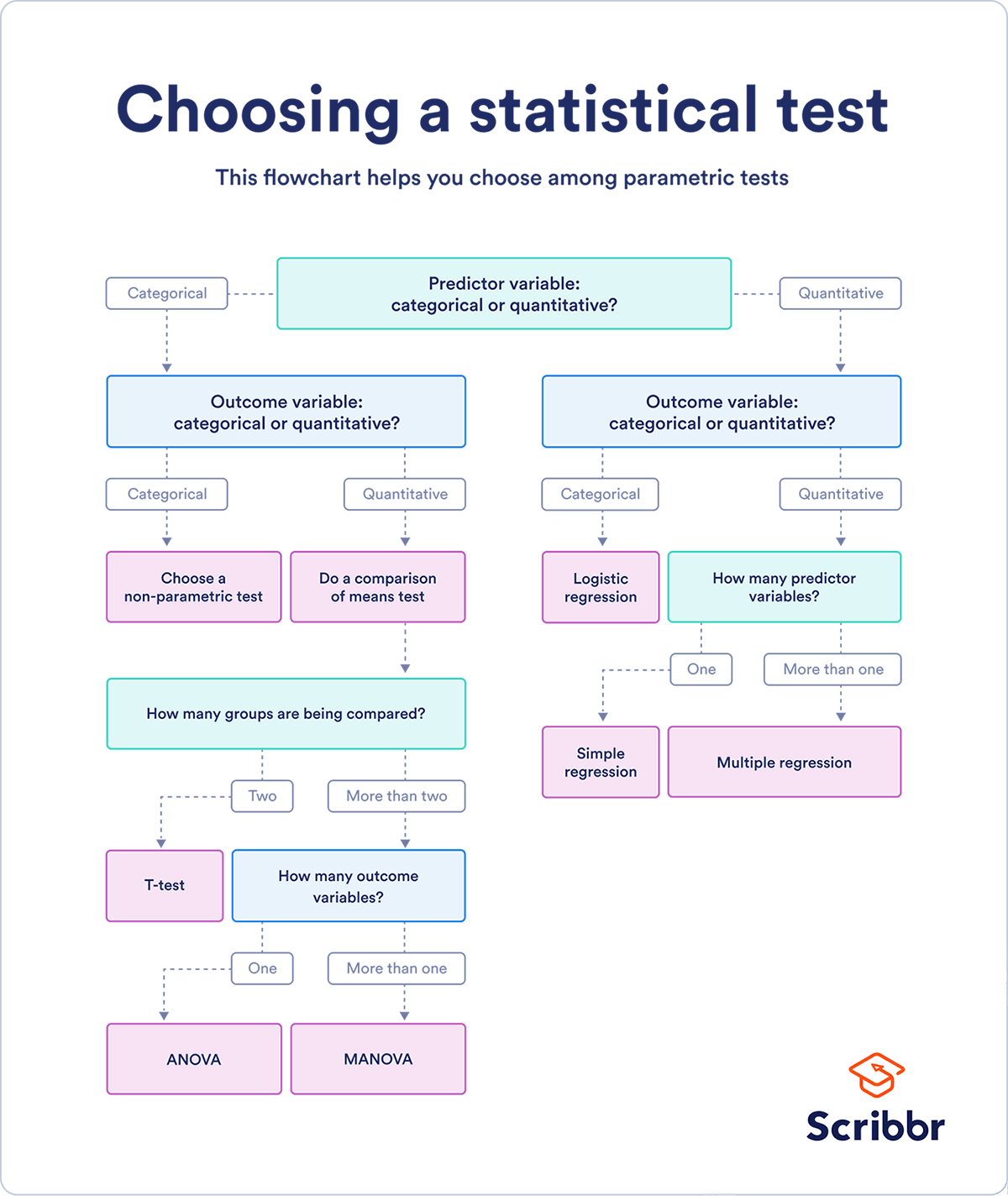
Choosing The Right Statistical Test Types And Examples
In non-statistical sampling the auditor does not quantify sampling risk.

. You can perform statistical tests on data that have been collected in a statistically valid manner either through an experiment or through observations made using probability sampling methods. Random selection of the sample. Provide an objective basis for quantitatively evaluating sample risks.
Instead conclusions are reached about populations on a more judgmental basis. On the off-chance that the populace individuals are unique or there are key things a non-statistical approach is. In addition both techniques are regarded as important for the determination of the sample size and the selection of the sample items.
This guideline applies to non-statistical sampling. In contrast to statistical audit sampling non-statistical audit sampling items are not chosen randomly. It can make sense to use non-statistical sampling when the population size is very small.
Both statistical and non-statistical approaches. The use of non-statistical sampling in audit sampling essentially removes this probability theory and is wholly dependent on the auditors judgment. Under what circumstances would you.
Any other approach is described as being non-statistical. This sampling method is called non-probability or non-statistical. Statistical sampling is any sampling that is done by random sampling methods and uses probability theory to measure the sample risk and evaluate the results of the sample.
The primary difference between non-statistical and statistical sampling is that non-statistical sampling relies more on the auditors judgment while statistical sampling relies on quantitative measurements to determine the sampling risk. A sampling approach that does not have characteristics i and ii is. It explains when and why sampling is used the factors considered indetermining if sampling will be used how sampling results are calculated and special situations that can affect sampling results.
And ii The use of probability theory to evaluate sample results including measurement of sampling risk. Statistical methods is more objective and representative in relation to the total population compared to the sample selected by non-statistical methods. Examine less than the total population to enable the auditor.
The a uthors explain the fundamental differenc es betw een them which consist. The auditor therefore quantifies sampling risk when statistical sampling is used. Sampling risk is the chance that the sample audit findings are.
While non-statistical sampling allows for auditor judgment an auditor should always be careful not to include. There are two types of sampling methods. If the population members are dissimilar or there are key items a non-statistical approach is most suitable.
Paper F8 students need to be able to differentiate between statistical and non-statistical sampling techniques. Statistical sampling is an approach to sampling that involves random selection of the sample items and the use of probability theory to evaluate the sample results including the measurement of sampling risk. GenevaMech- The difference in statistical vs non-statistical sampling is human bias.
Non-statistical sampling techniques are used more frequently than statistical sampling techniques for the evaluation of the sample. Statistical versus non-statistical sampling. When to Use Non-Statistical Sampling.
Please write a three to four page double-spaced paper incorporating the answers to the following questions make sure your answers are clearly indicated in your paper. Whereas its doesnt eradicate sampling danger statistical sampling permits the auditor to measure sampling danger and take steps to manage it. For a statistical test to be valid your sample size needs to be large enough to approximate the true distribution of the population being studied.
An approach to sampling that has the characteristics of being randomly selected and the use of probability theory to evaluate sample results. Non-probability sampling involves non-random selection based on convenience or other criteria allowing you to easily collect data. I hope this will help.
Define factors that affect the. Subjective Sampling In general the four most common non-probability sampling methods are convenience quota purposive and. A statistical technique gives an objective measure of hazard streamlines the example estimate and is best for a populace of countless exchanges.
ISA 530 provides the definition of statistical sampling as follows. Whereas non-statistical sampling is therefore any sampling approach that does not have both of the characteristicss of statistical sampling. Afford greater assurance than a non-statistical sample of equal size.
Statistical sampling is extra goal and makes use of chance to find out the suitable pattern dimension. An advantage of using statistical over non-statistical sampling methods in tests of controls is that the statistical methods a. An approach to sampling that has the following characteristics.
Statistical versus non-statistical sampling Statistical sampling allows each sampling unit to stand an equal chance of selection. Instead they are chosen based on the auditors judgment and the result of the testing from the selections is not used to infer the conclusion for the entire population. Click on to see full reply.
Statistical sampling is the use of mathematical measurement techniques to calculate formal statistical results. Some practitioners believe a statistical sample is more defensible. Analyse individual statistical and non-statistical methods of sampling the advantages and disadvantages of their use in practice.
Nonstatistical sampling depends extra on the auditors judgment. This approach is also useful in areas where specific records contain sensitive information and so must be examined. Particular on a nalyzing and comparing the statistical and non-statistical sampling method.
In this case it is not efficient to spend the extra time to set up a statistical sample. I Random selection of the sample items. Non-statistical sampling allows an auditor to use professional judgment when selecting samples.
Non-statistical methods make a lot of sense when a population is very small rather than spending the time setting up a statistical sample. G Statistical sampling An approach to sampling that has the following characteristics. Probability sampling involves random selection allowing you to make strong statistical inferences about the whole group.

Probability Sampling Methods This Ll Come In Handy When I Start Ph D Program Data Science Learning Statistics Math Research Methods

Types Of Sampling Methods Simple Techniques And Examples Social Science Research Social Work Research Research Methods

Strengths And Weaknesses Of Simple Random Sampling Compared To Other Probability Sampling Procedures Http Research Methods Probability Going Back To College
Comments
Post a Comment